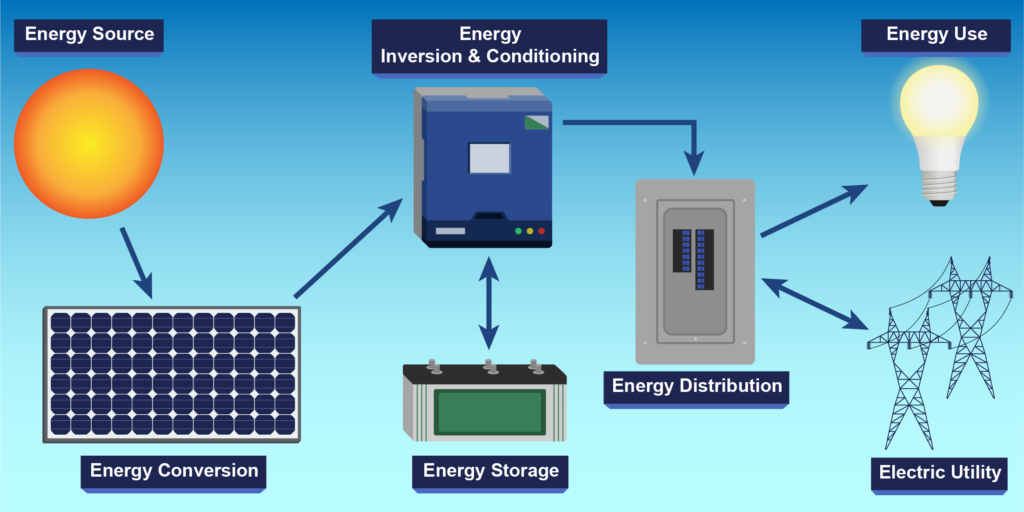
The relationship between solar panels, inverters, and batteries is crucial in the context of a solar power system with energy storage.
- Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Modules):
- Function: Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic modules, generate electricity from sunlight using the photovoltaic effect. When exposed to sunlight, the solar cells within the panels produce direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverters:
- Function: Inverters are essential components in a solar power system. They convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses.
- Types:
- Grid-Tied Inverters: These inverters are designed to synchronize with the electrical grid. They allow solar-generated electricity to be fed into the grid, reducing the need for electricity from the utility during sunny periods.
- Off-Grid Inverters: In off-grid systems, where there is no connection to the utility grid, off-grid inverters are used. They provide AC power to meet the electrical needs of the property and may also be connected to a battery system for energy storage.
- Batteries:
- Function: Batteries store excess electricity generated by solar panels for later use, typically when the sun is not shining, such as during the night or on cloudy days. They provide a way to store energy for later consumption and enhance the reliability and independence of the solar power system.
- Types:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Traditional and commonly used batteries in solar power systems. They are relatively affordable but have limitations in terms of lifespan and energy density.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These batteries are becoming increasingly popular for solar energy storage due to their higher energy density, longer lifespan, and better performance.
- Other Battery Chemistries: Various other battery chemistries are also used in solar energy storage systems, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
The Relationship:
- Solar Panels to Inverters:
- Solar panels generate DC electricity, and inverters convert this DC power into AC power that can be used to power appliances in a home or business. In grid-tied systems, excess electricity can be fed back into the grid.
- Inverters to Batteries:
- In off-grid or hybrid systems with energy storage, inverters are often connected to batteries. The inverter manages the charging and discharging of the batteries, ensuring a steady and reliable power supply.
- Solar Panels to Batteries:
- Excess electricity generated by solar panels during sunny periods is directed to charge the batteries. When the demand for electricity exceeds what the solar panels can generate, the stored energy in the batteries is used to meet the load.
- Battery Management:
- Charge controllers or battery management systems (BMS) are often employed to optimize the charging and discharging of batteries, protecting them from overcharging or overdischarging.
The integration of solar panels, inverters, and batteries allows for a more comprehensive and resilient solar power system. This combination is particularly beneficial in off-grid applications or areas with unreliable grid power, as it enables continuous access to electricity even when the sun is not shining. Additionally, solar power systems with batteries can provide backup power during grid outages.