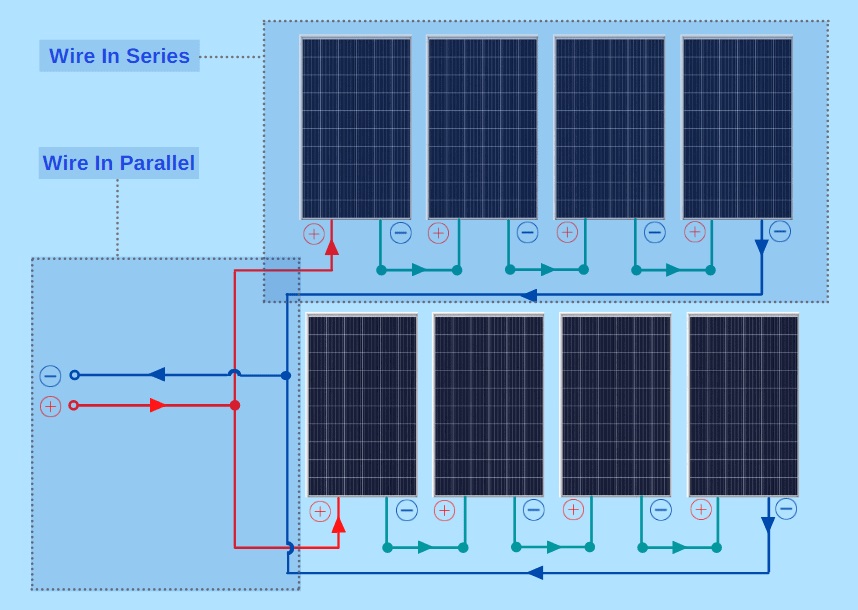
Solar panels with different voltages and currents can be connected in both series and parallel configurations, but there are important considerations to keep in mind when doing so.
- Series Connection:
- Connecting solar panels in series involves connecting the positive terminal of one panel to the negative terminal of another panel. This arrangement increases the total voltage output while keeping the current constant.
- When panels are connected in series, their voltages add up, but the current remains the same. This can be useful when you need to increase the voltage to match the requirements of your solar inverter or charge controller.
- However, when you connect panels in series, the overall system performance can be limited by the lowest-performing panel in the series. For example, if one panel is shaded or malfunctions, it can reduce the output of the entire series.
- Parallel Connection:
- Connecting solar panels in parallel involves connecting the positive terminals together and the negative terminals together. This arrangement keeps the voltage constant while increasing the total current output.
- Parallel connections are useful when you want to increase the current output of your system while maintaining the same voltage level. This can be important for maximizing energy production, especially in situations with limited roof space or shading issues.
- In a parallel configuration, the voltage remains the same across all panels, so the system’s performance is not limited by the lowest-performing panel. If one panel underperforms, it won’t significantly affect the others.
- Mixed Configurations:
- In some cases, you may use a combination of series and parallel connections to achieve the desired voltage and current levels for your specific system requirements. This is often done to optimize the efficiency and performance of the overall solar array.
When connecting solar panels with different voltages and currents, it’s crucial to ensure that the panels are compatible with each other and the rest of the system components (e.g., inverters, charge controllers). Mismatched panels can lead to suboptimal performance or potential damage to the system.
Additionally, properly designed and installed wiring configurations can help you make the most of your solar energy system while ensuring safety and reliability.