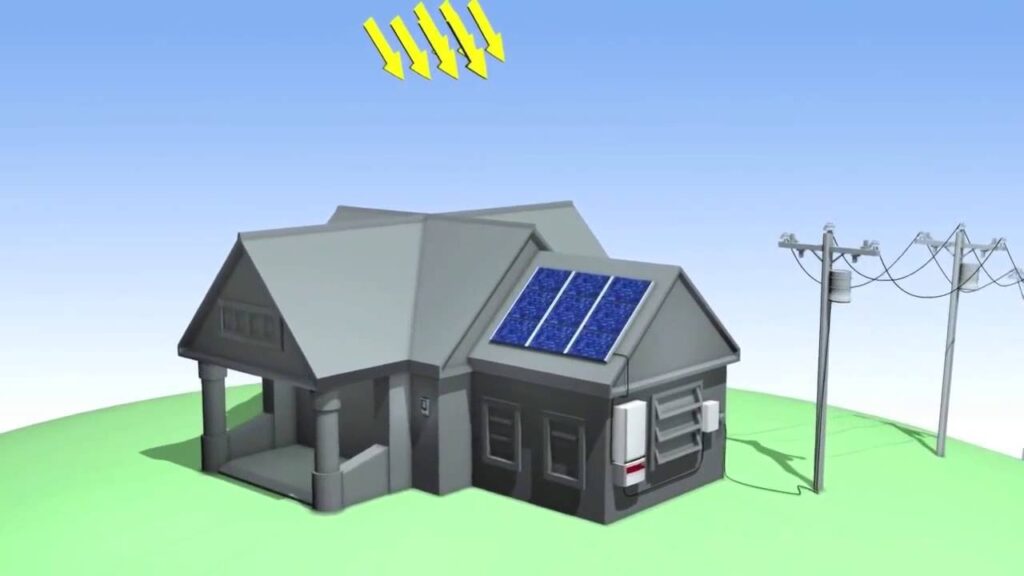
A grid-tied inverter is a device used in renewable energy systems, such as solar power or wind power systems, to convert direct current (DC) electricity generated by the renewable energy source into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be fed into the electrical grid.
- DC Power Generation: In a solar power system, for example, photovoltaic (PV) panels generate DC electricity when exposed to sunlight. This DC electricity is produced in varying amounts depending on factors like sunlight intensity and panel orientation.
- Inverter Input: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is fed into the input side of the grid-tied inverter.
- Inversion to AC: The grid-tied inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity. This is crucial because most electrical grids operate on AC power, and this is the form of electricity used in homes and businesses.
- Synchronization with Grid Frequency: The grid-tied inverter is designed to synchronize its output with the frequency and voltage of the electrical grid. This is essential to ensure that the electricity generated by the renewable energy system is compatible with the grid.
- Power Injection into the Grid: Once the inverter’s output is synchronized with the grid, it injects the AC electricity into the electrical grid. This electricity can then be used by nearby homes and businesses.
- Metering and Monitoring: In many grid-tied systems, there is often a meter installed to measure the amount of electricity generated by the renewable energy system. This information may be used for various purposes, such as calculating credits for the system owner or for grid management.
- Net Metering: In some regions, a system called net metering is used. If the renewable energy system generates more electricity than is being consumed at a particular moment, the excess electricity is fed into the grid, and the owner of the system may receive credits for this surplus energy. Conversely, when the system is not generating enough electricity, electricity can be drawn from the grid.
It’s important to note that grid-tied inverters typically do not provide power during a grid outage for safety reasons. This is to prevent the inadvertent energization of power lines during maintenance or repair work. To provide power during outages, additional equipment such as batteries and a backup inverter may be required.