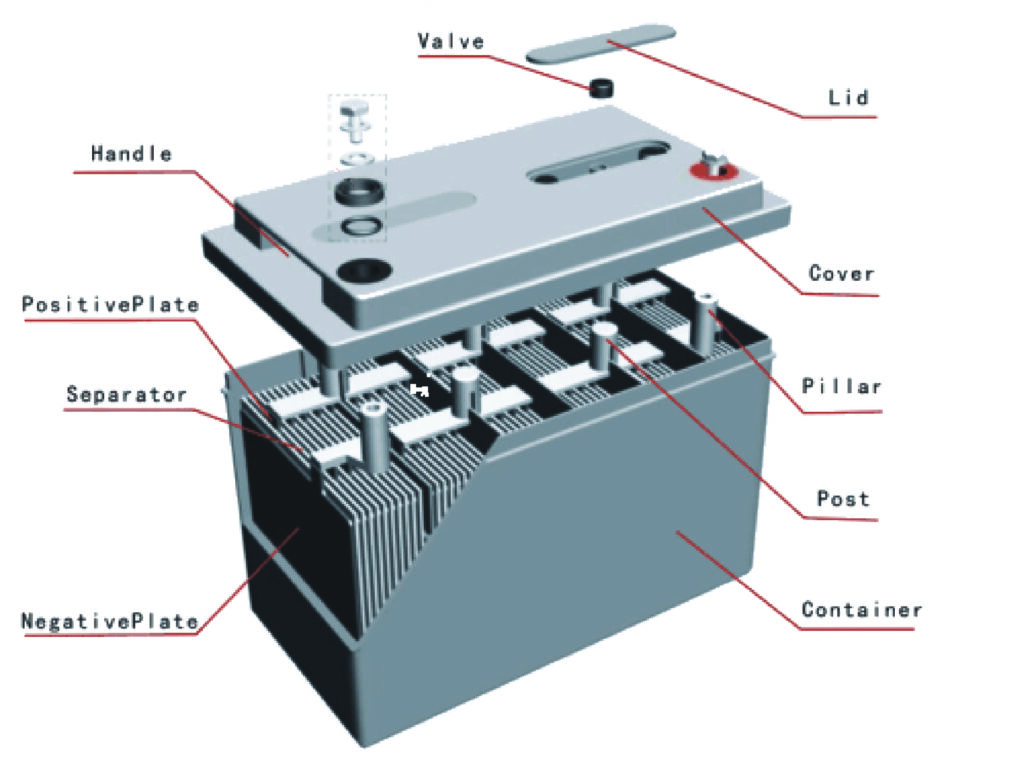
Lead-acid batteries, a common type of rechargeable battery, are widely used in various applications such as automotive, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, and renewable energy storage. The main performance parameters of lead-acid batteries include:
- Voltage:
- Nominal Voltage: The nominal voltage of a lead-acid cell is typically 2 volts. Common lead-acid batteries for automotive use are 12 volts (six cells in series), while larger batteries for backup power systems can be 24, 36, or 48 volts.
- Capacity:
- Ampere-Hour (Ah) Capacity: This parameter represents the total amount of charge a battery can store and deliver. It is often specified at a specific discharge rate (e.g., C/20, where C is the capacity in ampere-hours).
- Cycling Capability:
- Cycle Life: The number of charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly degrades. The cycle life of lead-acid batteries can vary based on factors like depth of discharge, charge/discharge rates, and operating conditions.
- Charge Efficiency:
- Charging Efficiency: The efficiency with which a lead-acid battery can accept charge. High charging efficiency is important to minimize energy loss during the charging process.
- Discharge Characteristics:
- Peukert’s Exponent: Describes how a lead-acid battery’s capacity decreases at higher discharge rates. A lower Peukert’s exponent indicates better performance at high discharge rates.
- Self-Discharge Rate:
- Self-Discharge: The rate at which a battery loses its charge when not in use. Lower self-discharge rates are desirable for applications where the battery may be idle for extended periods.
- Temperature Sensitivity:
- Temperature Performance: Lead-acid batteries have different performance characteristics at different temperatures. Manufacturers often provide temperature-dependent discharge and charge curves.
- Internal Resistance:
- Internal Resistance: The resistance within the battery that affects its ability to deliver high currents. Lower internal resistance results in better high-current performance.
- Float Voltage:
- Float Voltage: The voltage at which a lead-acid battery is maintained when not in use, typically during standby or float charge conditions. It prevents overcharging and helps extend battery life.
- Maintenance Requirements:
- Maintenance: Some lead-acid batteries are labeled as maintenance-free, while others may require periodic checks and maintenance, such as topping up electrolyte levels.
- Sulfation Resistance:
- Sulfation: The tendency of lead-acid batteries to form lead sulfate crystals on the plates, which can reduce capacity over time. Sulfation resistance is an important factor for prolonged battery life.
These parameters collectively define the performance characteristics of lead-acid batteries and help users select the appropriate type and size for specific applications.