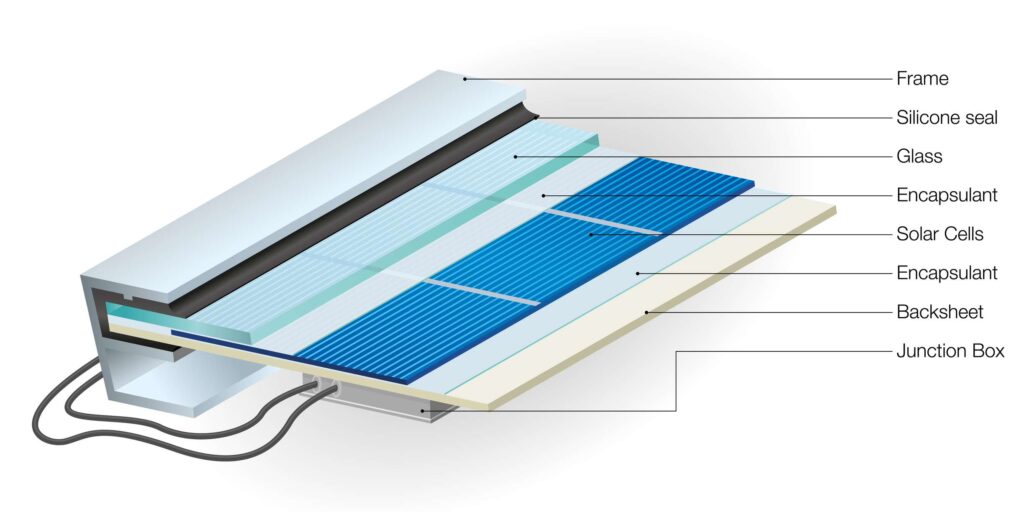
A solar panel, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) module, is composed of several key components that work together to convert sunlight into electrical energy.
- Solar Cells (Photovoltaic Cells):
- Function: Solar cells are the fundamental building blocks of a solar panel. They are semiconductor devices that directly convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When exposed to sunlight, the solar cells generate a direct current (DC) electrical voltage.
- Glass Cover:
- Function: The glass cover serves as a protective layer for the solar cells. It is typically made of tempered glass that is transparent to allow sunlight to pass through while providing physical protection against environmental factors.
- Anti-Reflective Coating:
- Function: An anti-reflective coating is often applied to the surface of the glass cover to minimize reflection and maximize the amount of sunlight that reaches the solar cells. This helps improve the overall efficiency of the solar panel.
- Solar Cell Encapsulation:
- Function: Solar cells are encapsulated to protect them from moisture, dust, and other environmental factors. Encapsulation materials, such as ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), are used to bond the solar cells to the glass cover and the backsheet.
- Backsheet:
- Function: The backsheet is the bottom layer of the solar panel, providing additional protection and insulation. It is typically made of a polymer material that is resistant to weathering and helps prevent moisture from entering the panel.
- Frame:
- Function: The frame provides structural support to the solar panel, helping to protect it from mechanical stresses such as wind and snow loads. It also facilitates the installation of the panel onto mounting structures.
- Junction Box:
- Function: The junction box is located on the back of the solar panel and houses electrical components such as diodes and connectors. It serves to connect the individual solar cells in the panel, manage the flow of electricity, and provide a point for electrical connections.
- Busbars:
- Function: Busbars are conductive strips or wires that collect the electrical current generated by individual solar cells and carry it to the junction box. They act as electrical highways, facilitating the efficient flow of current.
- Interconnectors (Ribbons):
- Function: Interconnectors are thin metal strips, often made of copper, that connect the individual solar cells within the module. They help in transferring the electrical current generated by each cell to the busbars and, ultimately, to the junction box.
- Frame Sealant:
- Function: A sealant is applied around the edges of the solar panel frame to prevent moisture from entering and to enhance the panel’s durability and weather resistance.
By working together, these components enable solar panels to harness sunlight and convert it into usable electrical energy for various applications.