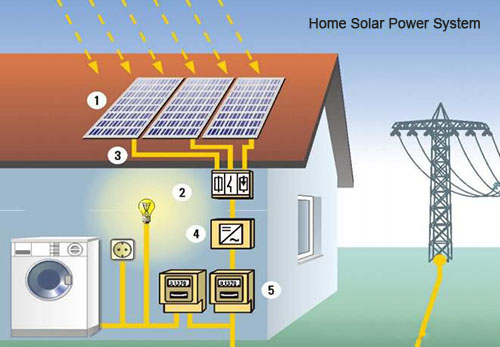
Household solar power generation involves harnessing the sun’s energy to generate electricity for residential use.
- Solar Panel Types: Understand the different types of solar panels available, such as monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, and choose the most suitable option based on your energy requirements, budget, and available space.
- Roof Suitability: Assess the orientation, tilt, and shading of your roof to determine its suitability for solar panel installation. Ideally, your roof should have sufficient space, proper orientation towards the sun, and minimal shading to maximize solar energy absorption.
- Energy Consumption Analysis: Conduct an energy audit of your household to evaluate your current energy consumption patterns. This analysis will help you determine the appropriate solar panel capacity needed to meet your energy requirements.
- Inverter Selection: Choose an appropriate inverter that can convert the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into usable alternating current (AC) for household appliances. Consider factors such as efficiency, reliability, and the type of inverter technology suitable for your solar system.
- Battery Backup (Optional): Decide whether you need a battery storage system to store excess solar energy for use during periods of low sunlight or power outages. Evaluate various battery options based on their capacity, lifespan, and efficiency.
- Net Metering and Grid Connection: Understand the concept of net metering, which allows you to sell excess electricity back to the grid, reducing your electricity bills. Check local regulations and policies regarding grid connection and feed-in tariffs to maximize your savings.
- Financial Considerations: Evaluate the upfront costs, available incentives, tax credits, and financing options for installing a solar power system. Calculate the return on investment (ROI) to determine the long-term financial benefits of switching to solar energy.
- Maintenance Requirements: Understand the maintenance needs of solar panels, including regular cleaning, inspection, and potential repairs. Develop a maintenance plan to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your solar power system.
- Local Regulations and Permits: Familiarize yourself with local building codes, zoning regulations, and permit requirements for installing a residential solar power system. Comply with all necessary regulations and obtain the required permits before beginning the installation process.
- Environmental Impact: Recognize the environmental benefits of using solar energy, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing reliance on non-renewable energy sources. Consider the positive impact of transitioning to clean energy for the environment and future generations.
By considering these essential aspects, you can make informed decisions when implementing a household solar power generation system, ultimately reducing your carbon footprint and enjoying long-term energy savings.